If you have a dog, chances are you have noticed a pungent smell coming from their rear at some point. You might have wondered why dogs anal glands produce such a strong odor and what it really means for their health.
As a veterinarian, I often encounter pet owners who are concerned, embarrassed, or confused about this topic. Why these glands smell, how to detect issues early, and what you can do to manage them is crucial for your dog’s comfort and hygiene.
Here, I will guide you through everything you need to know about dog anal glands in a practical, vet-approved way.
Anal glands, also called anal sacs, are small paired structures located just inside the rectum, at approximately four and eight o’clock positions.
They secrete a thick, foul-smelling fluid that is unique to each dog. This secretion serves as a way for dogs to communicate with each other, often signaling identity or reproductive status.
Despite their natural purpose, issues with these glands can cause discomfort, infection, or excessive odor, which makes it essential for owners to understand them.
The odor from anal glands is strong because it contains pheromones, oils, and other cellular debris.
This smell is natural and intended for communication among dogs. However, when the glands become full, impacted, or infected, the odor becomes much more noticeable to humans.
Dogs may also scoot, lick their rear, or display discomfort when their anal glands are problematic.
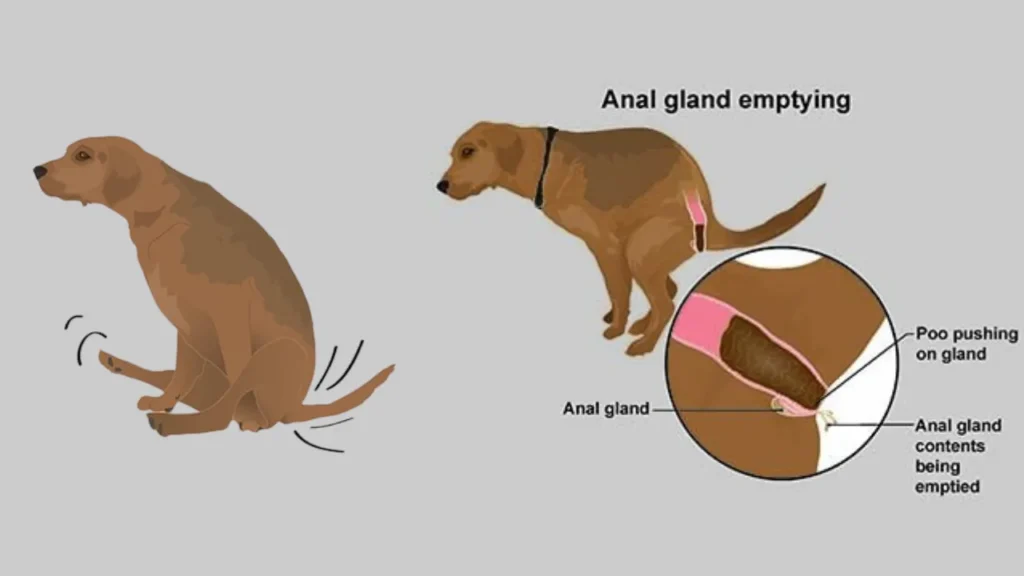
Anal gland issues are not uncommon, and several factors can contribute to them. Recognizing these causes early can prevent complications and improve your dog’s quality of life.
1. Dietary Factors
A dog’s diet significantly impacts anal gland health. Dogs with low-fiber diets often have softer stools, which fail to naturally express the glands during bowel movements. When anal glands are not emptied regularly, the fluid can thicken.
Consequently, it leads to blockage and foul odor. Feeding high-quality, fiber-rich foods or adding pumpkin to meals can help firm stools and naturally promote gland expression.
2. Breed Predispositions
Certain dog breeds are more prone to anal gland problems. Small breeds, such as Chihuahuas, Dachshunds, and Yorkshire Terriers, often struggle with impacted anal glands due to their smaller anatomy.
Even larger dogs, like Czech GSD, can experience issues, but smaller dogs typically need more frequent monitoring and possible manual expression.
3. Health Conditions and Infections
Bacterial diseases in dogs, infections, abscesses, or inflammation can worsen anal gland odor. Dogs with chronic diarrhea, obesity, or skin allergies may be more susceptible.
Signs of infection include redness around the anus, swelling, persistent licking, scooting, and a particularly strong, fishy odor. If left untreated, infections can become painful and lead to more serious complications requiring veterinary intervention.
Monitoring your dog’s behavior and physical signs can help catch anal gland issues early and help prevent infection and discomfort. So, what are these signs? Let’s learn about them below:
1. Behavioral Indicators
Dogs with anal gland discomfort often display scooting, licking, or biting at their rear. These behaviors indicate irritation and are usually one of the first signs of a problem. Some dogs may also exhibit restlessness, anxiety, or sudden reluctance to sit.

2. Physical Symptoms
Physically, you might notice swelling, redness, or a visible discharge near the anal opening. In more severe cases, abscesses can form, causing pain and requiring surgical drainage. Recognizing these symptoms early ensures timely treatment and prevents chronic issues.
No doubt, it is easier to prevent anal gland problems than to treat them once they occur. I recommend a proactive approach combining diet, hygiene, and professional care.
1. Dietary Management
A diet high in fiber helps naturally express anal glands during bowel movements. Many veterinarians suggest adding canned pumpkin or specialized fiber supplements to your dog’s meals.
Consistent feeding schedules also help regulate stool consistency, further aiding in gland expression. Also, it prevents intestinal blockage in dogs, which can lead to other complications.
2. Manual Expression
Manual expression involves gently pressing the glands to release the fluid. While some owners may learn to do this at home, I recommend having a veterinarian or trained groomer perform it initially to avoid injury.
Typically, manual expression is required when natural emptying fails, in small breeds or dogs prone to impaction.
3. Professional Veterinary Care
Regular veterinary checkups are essential for maintaining anal gland health. If a dog experiences frequent infections or chronic impaction, a vet may recommend further interventions such as flushing, antibiotics, or, in rare cases, surgical removal of the glands.
Never attempt surgery or aggressive manipulation at home, as this can cause serious injury.
4. Hygiene Practices
Keeping your dog’s rear clean and monitoring for discharge helps prevent infection. Wiping the area after bowel movements and checking for unusual odor or swelling can make a big difference.
Groomers can also assist with routine anal gland expression during regular trims, particularly for small or long-haired breeds.
Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial.
Persistent odor, swelling, or discharge requires veterinary evaluation. If your dog shows signs of pain, fever, lethargy, or blood in the stool, you should schedule an appointment immediately.
These symptoms may indicate bacterial diseases in dogs or abscesses, which require medical intervention. Timely care prevents complications, reduces discomfort, and ensures your dog maintains overall health and well-being.
Anal gland odor in dogs is natural but can indicate discomfort, impaction, or infection when strong or persistent. Understanding why these glands exist, how diet, breed, and health contribute to issues, and recognizing behavioral and physical warning signs helps pet owners manage this often-overlooked aspect of canine care.
Proactive measures, such as fiber-rich diets, manual expression, proper hygiene, and regular veterinary checkups, ensure your dog stays comfortable and healthy. Addressing anal gland problems promptly reduces pain, prevents infections, and improves your dog’s overall quality of life.
Paying attention to these small glands makes a big difference in your dog’s happiness.
